What is disaster management? Discuss about the detail process.
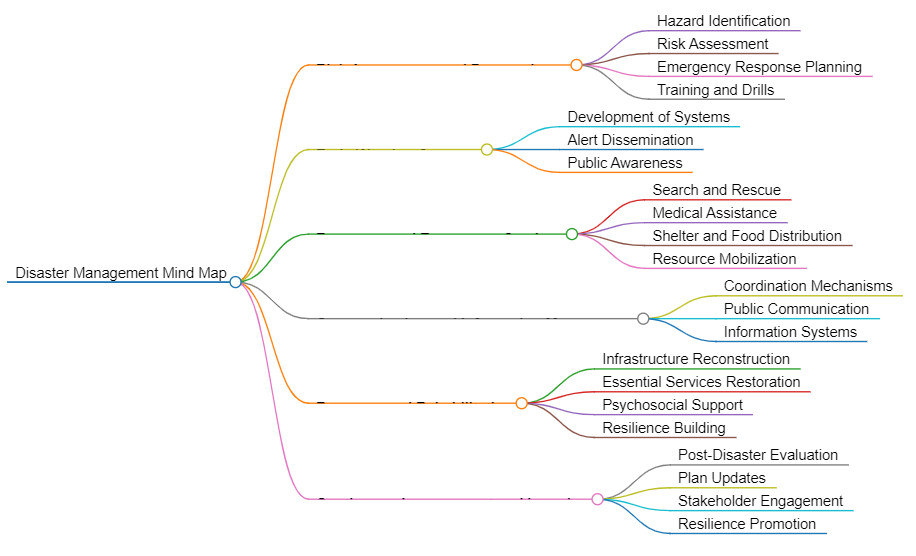
Disaster management involves various measures to mitigate the impact of disasters, both natural and man-made, and to facilitate effective response and recovery efforts. Here’s a brief outline of a disaster management plan:
1. Risk Assessment and Preparedness:
- Identify potential hazards and assess the risks associated with them.
- Develop emergency response plans tailored to different types of disasters (e.g., earthquakes, floods, pandemics).
- Conduct drills and training sessions to ensure that individuals and organizations are prepared to respond effectively in case of an emergency.
2. Early Warning Systems:
- Implement early warning systems to provide timely alerts about impending disasters.
- Ensure that warning messages are disseminated through various channels, including mobile alerts, sirens, and social media, to reach as many people as possible.
3. Response and Emergency Services:
- Establish coordination mechanisms among relevant government agencies, NGOs, and other stakeholders to facilitate a coordinated response.
- Provide emergency services such as search and rescue, medical assistance, shelter, and food distribution to affected populations.
- Mobilize resources, including personnel and equipment, to support response efforts.
4. Communication and Information Management:
- Establish communication networks to facilitate information sharing and coordination among response agencies.
- Provide accurate and timely information to the public about the disaster situation, evacuation routes, emergency shelters, and available services.
- Utilize technology, such as GIS mapping and satellite imagery, to collect and analyze data for decision-making purposes.
5. Recovery and Rehabilitation:
- Develop plans for the recovery and rehabilitation of affected communities, including rebuilding infrastructure, restoring essential services, and providing psychosocial support to survivors.
- Coordinate with international organizations and donors to secure funding and technical assistance for reconstruction efforts.
- Promote long-term resilience through measures such as land-use planning, building code enforcement, and community-based disaster risk reduction initiatives.
6. Continuous Improvement and Learning:
- Conduct post-disaster evaluations to identify lessons learned and areas for improvement.
- Update disaster management plans and procedures based on feedback and emerging threats.
- Foster a culture of resilience by engaging stakeholders in ongoing preparedness and mitigation efforts.